Sample Required: Urine | Test Type: Toxicity
Key Advantages
Porphyrins vs Pyrroles?
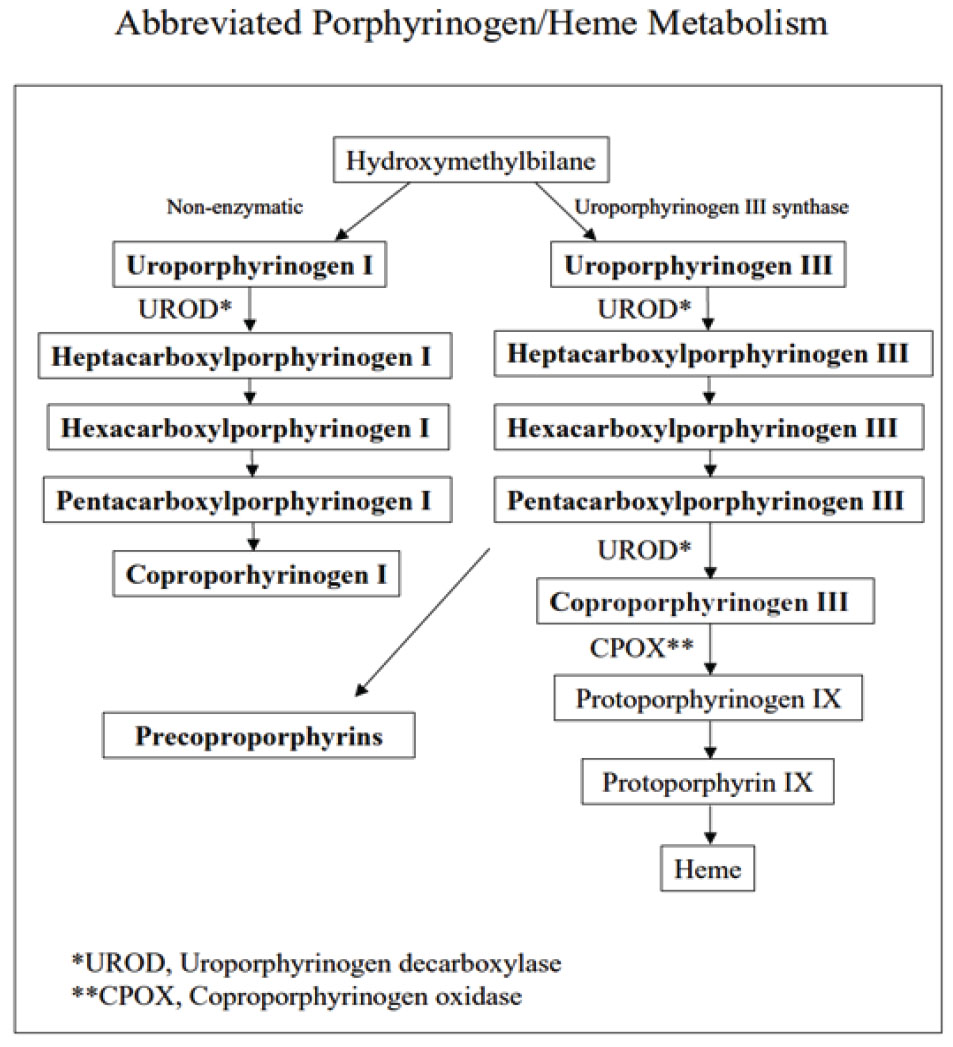
Urinary porphyrins are intermediary metabolites of heme biosynthesis and can serve as biomarkers of certain disorders in heme production and toxic burden. Heme is incorporated into becoming Hemoglobin protein (the oxygen carrying molecule in the blood) but also is essential in supporting energy production via the electron transport chain and liver detox. Heme biosynthesis begins with the formation of alpha-aminolevulonic acid from succinyl-CoA and glycine with pyridoxal-5-phosphate as an obligatory co-factor. Thereafter, a series of enzymatic and non-enzymatic reactions produce various porphyrins and Heme.
Abnormal porphyrin profiles have been associated with genetic disorders, metabolic disturbances/diseases, nutritional status, oxidative stress, and exposure to toxic chemicals or toxic elements such as arsenic, lead or mercury.
Abnormal urinary porphyrins associated with xenobiotics include mercury; pentacarboxylporphyrinogen, coproporphyrinogen III and sometimes precoproporphyrins, arsenic; high ratio of copro I:III, uroporphyrins I & III, organic chemicals; uroporphyrins, heptacarboxylpophyrins, pentacarboxylporphyrin, coproporphyrin III. Oxidation of the abnormally elevated porphyrinogens results in elevated total urinary levels of total porphyrins, pentacarboxylporphyrins and coproporphyrin III.
Various drugs and other substances can suppress enzymes involved in porphyrin metabolism and affect the levels of porphyrins. Such compounds include alcohol, sedatives, analgesics, antibiotics, estrogens and oral contraceptives. Anaemia, pregnancy, and liver disease can also affect porphyrin metabolism.
The Urine Porphyrins test essentially looks to see if urine porphyrin ring compounds are being spilled into the urine. This provides us with an inference into how much certain metabolic enzymes are being disturbed (functional assessment) by various compounds in the body. This might be due to a presence of a toxin or a genetic block. Either way, these key enzymes are not metabolising correctly/sufficiently to subsequent metabolites to bring about Heme.
Anyone who may have any genetic errors of metabolism or exposed to a toxin (metal/chemical)
(Check to what degree their metabolism is disturbed and use a process of elimination of how you can best compensate for that block).
This tree summarises the metabolite markers in the order of the cascade that it follows to become Heme. Two steps up from Hydroxymethylbilane, Glycine conjugates with Succinyl-CoA to make the starting compound for this cascade via pyridoxal-5-phosphate (vitamin B6). Ample supply of these may be a consideration.