Sample Required: Saliva | Test Type: Hormone
Key Advantages
Introduction
Saliva testing measures the “unbound” biologically active or free hormone levels in the body:
When blood is filtered through the salivary glands, the bound hormone components are too large to pass through the cell membranes of the salivary glands. Only the unbound hormones pass through and into the saliva. What is measured in the saliva is considered the “free”, or bioavailable hormone, that which will be delivered to the receptors in the tissues of the body.
Blood testing measures the “protein-bound” hormone levels in the body:
Usually, for steroid hormones to be detected in serum, they must be bound to circulating proteins. In this bound state, they are unable to fit into receptors in the body, and therefore will not be delivered to tissues. They therefore usually reflect the current reserve amount of hormone available (rather than the current active hormone).
Why test hormone levels?
Hormones are powerful molecules essential for maintaining physical and mental health. We frequently think of estrogen as being a female hormone, and testosterone as being a male hormone. But men AND women make both, plus several more that need to be in balance for optimum health. An imbalance of any one hormone can throw your physical and mental health out of balance, causing aggravating and even serious health problems.
One size does not fit all when it comes to hormones! For decades modern medicine has often prescribed hormone replacement therapy as if everyone needed the same forms and the same amount. Nothing could be further from the truth. Your hormones are like your fingerprints and in order to achieve optimal health, you need to know what your specific imbalances are.
Pooled Tube Provides More Accurate Sex Hormone Levels
Sex hormone (E2, Pg, T, DHEA) levels fluctuate throughout the day as well as throughout the month while other hormones, like cortisol, have a predictable diurnal rhythm. As a result, many blood test measurements will give falsely elevated or depressed values if only evaluating one sampling for sex hormones.
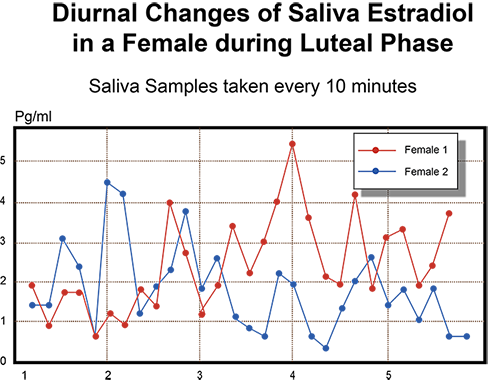
The graph below shows the measured salivary estradiol levels (in pg/ml) of two females during the luteal phase, with samples taken every 10 minutes. As you can see, the estrogen levels are fluctuating continuously and dramatically. Imagine if you had only measured one sampling… say in the morning? It might alter your assessment and lead you to incorrect treatment choices.
Labrix Measures Sex Hormones From a Fifth Pooled Tube
When saliva kits are received by our lab, a fifth tube of saliva is created by pooling a measured sample from each of the four submitted tubes. This fifth pooled tube is mixed thoroughly to provide homogenization and becomes the source from which estradiol, progesterone, testosterone and DHEA are measured. The pooling of these multiple samples throughout the day enables us to provide a much better reflection of each patient’s hormonal status. It is essentially an average of the four submitted samples and more accurately reflects the physiologic hormone levels.
Cortisol Levels Are Measured From Four Timed Samples
Cortisol levels are measured from the original four saliva tubes to provide an assessment of the natural diurnal rhythm of cortisol. Cortisol should be highest in the morning, and gradually taper off throughout the day. Knowing the time of day that a sample was collected is critical to accurate interpretation of the cortisol levels.
Melatonin is Measured From Three Timed Samples
Like cortisol, melatonin is measured directly from the AM, evening and PM sample. Melatonin levels follow a diurnal rhythm with highest levels produced at night, when sleep should be occurring, and the lowest levels should be during daytime.
The Comprehensive Plus Panel expands on the Comprehensive Hormone Panel and includes estrone (E1) and estriol (E3) plus the Estrogen Quotient. The Estrogen Quotient (EQ) is a simple ratio of the cancer protective E3 to the proliferative estrogens E1 and E2. The EQ provides an assessment of breast cancer risk, with a lower number (<1.0) indicating increased risk, and a higher number (>1.0) signifying a lower risk. For maximum protection, an optimal EQ is >1.5. Because the research on the Estrogen Quotient and the protective properties of estriol has not been done with men, this panel is currently recommended for women only. This panel should be considered for patients who have:
A comprehensive preventative breast health program extends beyond imaging and lifestyle optimisation, and includes accurate assessment and comprehensive treatment of demonstrated hormone imbalances. Labrix offers the Women’s Health and Breast Panel as an accurate, non-invasive tool to advance risk prevention and support you in providing exceptional care to your patients.
The Women’s Health and Breast Panel evaluates foundational hormone and adrenal status. This panel provides an in-depth look at estrogen levels, conversion patterns and offers two risk assessment ratios (Estrogen Quotient and PG/E2 Ratio) and also a customised women’s health and breast health specific interpretation. This additional clinical information is essential to further the conversation with your patients about targeted treatment options such as BHRT, nutraceutical and herbal supplementation, as well as potential lifestyle modifications.
The Comprehensive Hormone Panel is the starting point for initial assessment of hormonal status and endocrine function and includes estradiol (E2), progesterone, testosterone, DHEA and four cortisols. This panel is useful with male and female patients because it looks at the full diurnal cortisol pattern; it is especially important in patients who are experiencing the following symptoms in addition to the symptoms listed for the Basic Hormone Panel:
This assessment is useful in men and women whose primary symptoms are related to sex hormone imbalances (elevated or depressed E2, P or T). The abbreviated adrenal panel that includes DHEA and the AM and PM cortisol levels provides a brief assessment of the level of involvement of adrenal dysfunction. Additionally, this condensed panel (like the Basic Hormone Panel) is often used for re-evaluation 2-3 months after hormone replacement has begun to monitor therapeutic values. The Short Comprehensive Panel should be ordered if the patient is suffering from:
the full diurnal cortisol pattern; it is especially important in patients who are experiencing the following symptoms in addition to the symptoms listed for the Basic Hormone Panel:
The Basic Hormone Panel provides a basic evaluation of the sex hormones and a brief glimpse at adrenal function with the AM cortisol level. This panel is useful when retesting patients who have begun hormone therapy, but we encourage use of the Comprehensive Panel for initial evaluation. This is the minimal test recommended for symptoms that include:
Men Experiencing:
Women Experiencing:
t of the level of involvement of adrenal dysfunction. Additionally, this condensed panel (like the Basic Hormone Panel) is often used for re-evaluation 2-3 months after hormone replacement has begun to monitor therapeutic values. The Short Comprehensive Panel should be ordered if the patient is suffering from:
the full diurnal cortisol pattern; it is especially important in patients who are experiencing the following symptoms in addition to the symptoms listed for the Basic Hormone Panel:
This panel provides a comprehensive view of adrenal function and includes 4 cortisol levels timed throughout the day as well as DHEA. Symptoms that would indicate ordering this panel include:
This panel is similar to the Adrenal Function Panel, but would be used in patients who do not require DHEA testing.
The Melatonin Panel provides a snapshot of the sleep/wake cycle during a one day period. This panel (also can be added on to any saliva panel) is recommended for those experiencing sleep disturbances.
Choose your own personalised panel: E1, E2, E3, Pg, T, D, C, M, sIgA
The major sex hormones to assess are estradiol, progesterone and testosterone. Estrone and estriol are also important sex hormones to consider testing. The main adrenal hormones are DHEA and cortisol. These seven hormones will provide crucial information about deficiencies, excesses and daily patterns, which then result in a specifically tailored treatment approach and one far more beneficial than the old “shotgun” approach. Below is a brief description of each of these hormones:
Estrogens:
There are three forms made by the body: estrone, estradiol and estriol. The form used in past hormone replacement therapies is estradiol, often in the form of concentrated pregnant mare’s urine (premarin). It is a proliferative (causes growth) hormone that grows the lining of the uterus. It is also a known cancer-causing hormone: breast and endometrial (uterine) in women and prostate gland in men. It will treat menopausal symptoms like hot flashes, insomnia and memory-loss. With bio-identical formulas estriol is often matched with estradiol (biest) to provide protective effects and additional estrogenic benefits. The other major protector in keeping estradiol from over-running the system, is progesterone. Estrone and estriol are also useful hormones to test.
Progesterone:
Called the anti-estrogen because it balances estradiol’s proliferative effects. It is considered preventive for breast and prostate cancers as well as osteoporosis. In addition, too little progesterone promotes depression, irritability, increased inflammation, irregular menses, breast tenderness, urinary frequency and prostate gland enlargement (BPH).
Testosterone:
An anabolic hormone (builds tissue) that is essential for men and women. The proper level of testosterone is necessary for bone health, muscle strength, stamina, sex drive and performance, heart function and mental focus.
DHEA:
An important adrenal gland hormone, which is essential for energy production and blood sugar balance. DHEA is a precursor to other hormones, mainly testosterone.
Cortisol:
Your waking day hormone (highest in the morning and lowest at night). It is necessary for energy production, blood sugar metabolism, anti-inflammatory effects and stress response.
Melatonin:
Classified as a hormone but also acting as a neurotransmitter, melatonin is primarily secreted during the dark (at night) with levels dropping dramatically after exposure to bright light. Melatonin is involved with circadian rhythms, and most commonly associated with sleep patterns and sleep disturbances.
Some of the common imbalances identified through hormone testing include estrogen dominance, estrogen deficiency, progesterone deficiency, androgen (testosterone and DHEA) excesses or deficiencies, adrenal dysfunction and adrenal fatigue.