Sample Required: Stool | Test Type: Immunity
The GI360™ Profile is an innovative, comprehensive and clinically applicable stool profile, utilising new evidence-based DNA mapping technology coupled with growth-based culture and ID by MALDI-TOF, sensitive biochemical assays and microscopy. The ultimate combination to detect and assess the status of pathogens, viruses, parasites and bacteria that may be contributing to acute or chronic gastrointestinal symptoms and disease.
Specifically developed to provide clinically actionable results, including standardised dysbiosis index and live susceptibility testing, this breakthrough test utilises the widest array of highly validated technologies in one test.

It is important to continue testing culture alongside using DNA methods.
Culture is considered the gold standard for stool microbiology, and is the only method that allows isolating organisms for standardised antimicrobial susceptibility testing, and facilitates advanced MALDI-TOF species identification.
only method that allows isolating organisms for standardised antimicrobial susceptibility testing, and facilitates advanced MALDI-TOF species identification.
Traditionally in Microbiology there are 3 different growth conditions considered. Doctors Data looks at 10 different growth conditions.
When there are deficiencies in expected bacteria, mucosal barriers are compromised, which can result in:
MALDI-TOF is utilised to identify specific pathogenic and dysbiotic species. At Doctor’s Data they ensure accurate results through regular equipment calibrations and highly skilled technicians.
identify specific pathogenic and dysbiotic species. At Doctor’s Data they ensure accurate results through regular equipment calibrations and highly skilled technicians.
MALDI-TOF ID of Cultured Bacteria and Yeast
This microbiology testing is able to identify more than 1400 organisms, including imbalanced and pathogenic bacteria. MALDI-TOF technology is “open database”, so it can identify unlimited new organisms.
What is it?
MALDI-TOF is a laser technology that allows for higher specificity of identification because it is looking for the “finger-print” which is unique to a particular organism. There are 5 steps in the MALDI-TOF MS identification process:
Ensures targeted & effective treatment
Using the pathogens detected by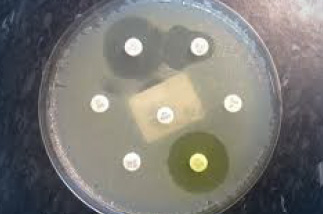 MALDI-TOF, EVERY single patient’s sample is tested using the diffusion method to identify the zones of inhibition which are unique to each patient – evaluating phenotypic expression, for reliable eradication strategies (including yeasts). Doctor’s Data includes both pharmaceutical agents as well as botanicals in their susceptibility testing.
MALDI-TOF, EVERY single patient’s sample is tested using the diffusion method to identify the zones of inhibition which are unique to each patient – evaluating phenotypic expression, for reliable eradication strategies (including yeasts). Doctor’s Data includes both pharmaceutical agents as well as botanicals in their susceptibility testing.
What is Tested?
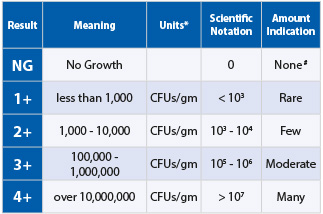 The simplification of scientific notations
The simplification of scientific notations
Doctors Data simplify the report by marking the colony forming units (CFU’s) as
1+ to 4+ for MALDI-TOF results. (These indicate the scientific notation range):
1+ = <103 | 2+ = 103-104 | 3+ = 105-106 | 4+ = >107
DNA results are represented in standard deviations (-3 to +3)
 What is it?
What is it?
The Microbiome Abundance and Diversity test is a standardised, reproducible, and clinically validated test that gives a birds eye view of the gut Microbiome. It is the most relevant gut microbiota DNA analysis tool and identifies and characterises the abundance and diversity of more than 45 targeted analytes that peer-reviewed research has shown to contribute to dysbiosis and other chronic disease states. This test cuts out the noise by representing only the most relevant markers that distinguish between normobiosis and dysbiosis.
This data is collected by Multiplex PCR 16sRNA
The technology has a higher specificity to capture a varied range of organisms in the patient’s stool and can get down to the specific sub-species compared to other PCR methods which are less specific. This allows for more accurate and reproducible identification of what is actually in the patients sample. The technology used has several research papers in supporting it’s validity behind identification of particular species for IBS & IBD. This is Multiplex PCR testing, measuring Microbiome bacterial abundance and diversity, through DNA analysis of 45+ organisms.

Why is it important to test?
Yeast are not uniformly dispersed throughout the stool and this may lead to undetectable or low levels of yeast identified by microscopy, despite culture and identified yeast species. Conversely, microscopic examination may reveal a significant amount of yeast present but no viable yeast cultured. Yeast may not always survive through the intestines. Nonviable diet-derived yeast may also be detected microscopically.
Why is it important to test?
SCFAs are the end product of the bacterial fermentation process of dietary fibre by beneficial flora in the gut and play an important role in the health of the GI as well as protecting against intestinal dysbiosis. Lactobacilli and bifidobacteria produce large amounts of SCFAs, which decrease the pH of the intestines and therefore make the environment unsuitable for pathogens, including bacteria and yeast. Studies have shown that SCFAs have numerous implications in maintaining gut physiology. SCFAs decrease inflammation, stimulate healing, and contribute to normal cell metabolism and differentiation. Levels of Butyrate and Total SCFA in mg/mL are important for assessing overall SCFA production, and are reflective of beneficial flora levels and/or adequate fibre intake.
bacterial fermentation process of dietary fibre by beneficial flora in the gut and play an important role in the health of the GI as well as protecting against intestinal dysbiosis. Lactobacilli and bifidobacteria produce large amounts of SCFAs, which decrease the pH of the intestines and therefore make the environment unsuitable for pathogens, including bacteria and yeast. Studies have shown that SCFAs have numerous implications in maintaining gut physiology. SCFAs decrease inflammation, stimulate healing, and contribute to normal cell metabolism and differentiation. Levels of Butyrate and Total SCFA in mg/mL are important for assessing overall SCFA production, and are reflective of beneficial flora levels and/or adequate fibre intake.
Butyrate is a major regulator of mucosal barrier integrity and mediates the release of anti inflammatory cytokines by epithelial cells. It is fuel for enterocytes, and it also mediates microbial cross talk.
 Why is it important to test?
Why is it important to test?
Inflammation can significantly increase intestinal permeability and compromise assimilation of nutrients. The extent of inflammation, whether caused by pathogens or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), can be assessed and monitored by examination of the levels of biomarkers such as lysozyme, lactoferrin, white blood cells and mucus via this stool test.
These markers can be used to differentiate between inflammation associated with potentially life-threatening inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), which requires lifelong treatment, and less severe inflammation that can be associated with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) which is frequently due to the presence of enteroinvasive pathogens. Lactoferrin is only markedly elevated prior to and during the active phases of IBD, but not with IBS. Monitoring faecal lactoferrin levels in patients with IBD can therefore facilitate timely treatment of IBD, and the test can be ordered separately.
Why is it important to test?
sIgA is secreted by mucosal tissue and represents the first line of defense of the GI mucosa and is central to the normal function of the GI tract as an immune barrier. Elevated levels of sIgA have been associated with an upregulated immune response.
defense of the GI mucosa and is central to the normal function of the GI tract as an immune barrier. Elevated levels of sIgA have been associated with an upregulated immune response.
If there is elevated sIgA levels when there is dysbiosis or a parasite present, this indicates that there is a normal immune response.
If there is low sIgA when there is dysbiosis or a parasite present, it may indicate a lowered immune response – therefore improving gut immunity should be prioritised.
Elastase – Elastase findings can be used for the exclusion of pancreatic insufficiency. Correlations between low levels and chronic pancreatitis and cancer have been reported. Decreased Elastase may also be seen in alcoholism or a past history of alcoholism.
used for the exclusion of pancreatic insufficiency. Correlations between low levels and chronic pancreatitis and cancer have been reported. Decreased Elastase may also be seen in alcoholism or a past history of alcoholism.
Fat Stain – Microscopic determination of faecal fat using Sudan IV staining is a qualitative procedure utilised to assess fat absorption and to detect steatorrhea.
Muscle Fibres – Muscle fibres in the stool are an indicator of incomplete digestion. Bloating, flatulence, feelings of “fullness” may be associated with increase in muscle fibers.
Vegetable Fibres – Vegetable fibres in the stool may be indicative of inadequate chewing, or eating “on the run”.
Carbohydrates – The presence of reducing substances in stool specimens can indicate carbohydrate malabsorption.
 What is it?
What is it?Beta-glucuronidase is an enzyme that breaks the tight bond between glucuronic acid and toxins in the intestines. The binding of toxins in the gut is protective by way of blocking their absorption and facilitating excretion.
Higher levels of beta-glucuronidase may be associated with an imbalanced intestinal microbiota profile, as well as higher circulating oestrogens and lower faecal excretion of oestrogens.

GI360 utilises multiplex DNA technology, testing for multiple pathogens and parasites (for which genetic probes exist for), to assist with identification.

Gold standard parasitology involves a qualified parasitologist examining 3 consecutive stool samples via microscopy to detect all forms of parasites (including their egg stages), for the most conclusive assessment of parasite presence.